Yesterday, we posted about Northwestern University‘s work with various extraterrestrial regolith soil simulants. We decided to get in touch with the team behind the project for a follow-up on the state of this research and clarifications about certain elements of the methodology.
Our interviewee, Adam Jakus, has a Ph.D. in Materials Science and Engineering and is an expert on advanced material functional inks, ceramics, polymers and composites. We were able to contact Adam, as he is one of the lead researchers on the project, and he was kind enough to answer our questions.
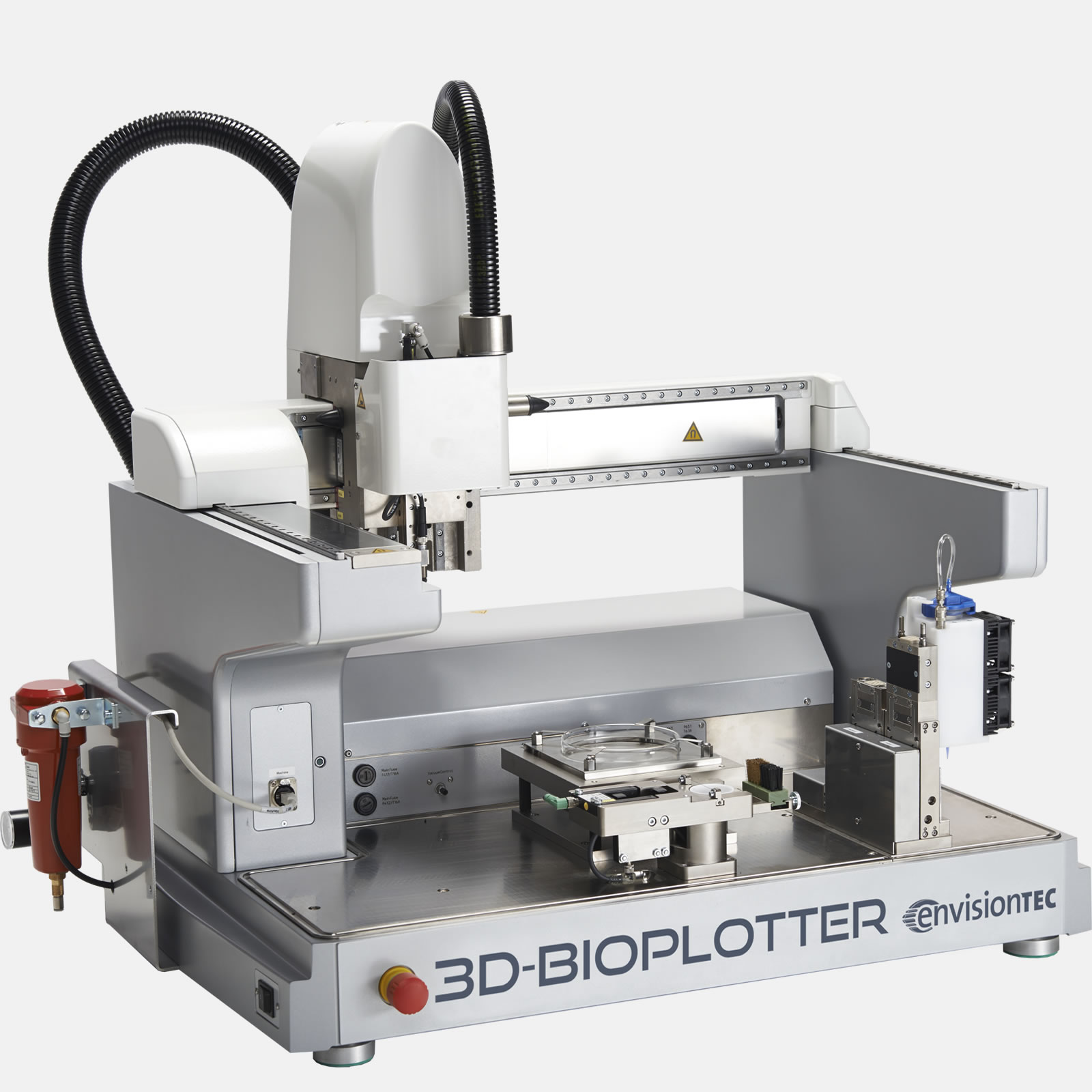
1) What types of printers are you using for processing the lunar soil and martian soil simulants? and how does the process differ from standard 3D painting?
[For] this work we used an EnvisionTEC 3D-BioPlotter to 3D-print (simple extrusion) the Lunar and Martian inks. However, the Lunar and Martian inks we developed could be 3D-printed on any extrusion-based 3D-printer. Our laboratory focuses on developing new materials for 3D-printing, and as such, there is nothing particularly special or unique about the 3D-printer (hardware) used.
It’s all about the materials design. Our laboratory invented the “3D-painting” process and approach, and thus, there technically is no standard 3D-painting. We have demonstrated the ability to use this process to create a very extensive variety of 3D-printable inks including metals and alloys, graphene (3D-Graphene) and carbon nanotubes, ceramics, biomaterials (Hyperelastic “Bone”), etc. (these new materials were previously reported on the in the media extensively). Thus, on one extrusion-based 3D-printer, many types of materials can be very quickly 3D-printed.
2) Are the printers using their stock parts as developed by a manufacturer on request or has your team modified them personally. If yes, then how so?
There is nothing special about the 3D-printer itself used in this work, and no modifications were made. It is a commercially available 3D-Bioplotter, but the inks could be used with any extrusion-based 3D-printer. The Lunar and Martian inks are an extension of the 3D-paintable materials we have previously developed and described.
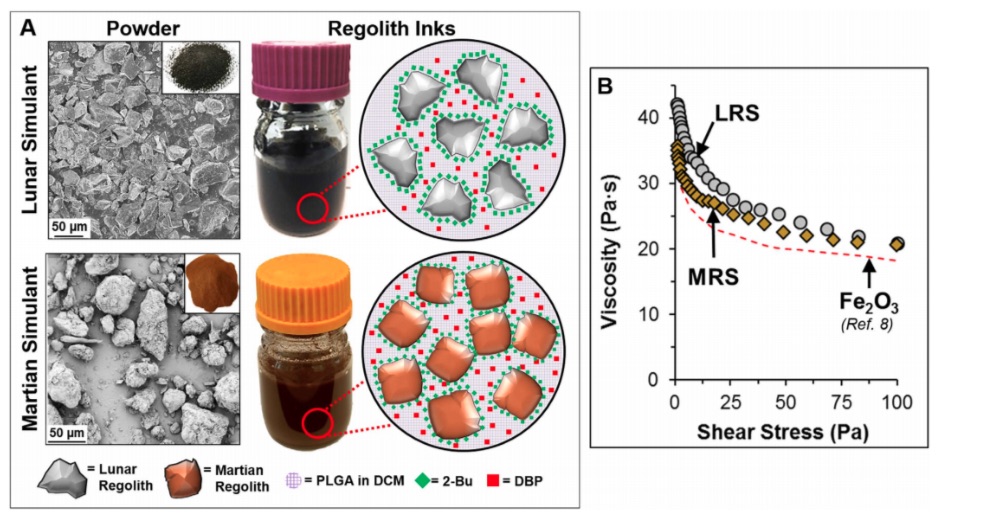
3) I read that the simulants were made with a combination of commercially available materials. How did your team develop them (methodology, equipment) and in what ways do these materials differ from actual martian and lunar soil?
The Martian and Lunar Regolith simulant powders were commercially available, as are all the other components of the inks. We created the Lunar and Martian inks using our 3D-paint approach.
The simulants are the same the same simulant powders used by NASA and space researchers, and were developed specifically for extraterrestrial research. They are quite close in both composition and particle size/shape to those found on Mars and the Moon. The Martian regolith is rough, but rounded, due to weathering (Mars has an atmosphere and wind). The Lunar regolith is sharp and jagged (no weathering, and was produced by meteor and asteroid impacts). The simulants simulate these powders quite well.
4) What other hurdles are necessary before the technology is space-flight ready?
It is primarily dependent on the 3D-printing hardware, and for manufacturers to create additional space-flight ready extrusion based 3D printers (similar to the one already on the international Space Station).
A special thanks to Adam Jakus for answering all our questions. The research manuscript is available here.
Adam Jakus, PhD
Hartwell Postdoctoral Fellow Northwestern University | Ph.D. Materials Science and Engineering
Georgia Institute of Technology | B.S. and M.S. Materials Science and Engineering
Research Interests: Engineering and 3D-printing new metal, ceramic, polymer, composite, and advanced material functional inks. Developing new multi-material printing techniques. Design and implementation of 3D-printing enabled materials and devices for medical, structural, and energy applications.